The Chinese stock market in 2021-2024
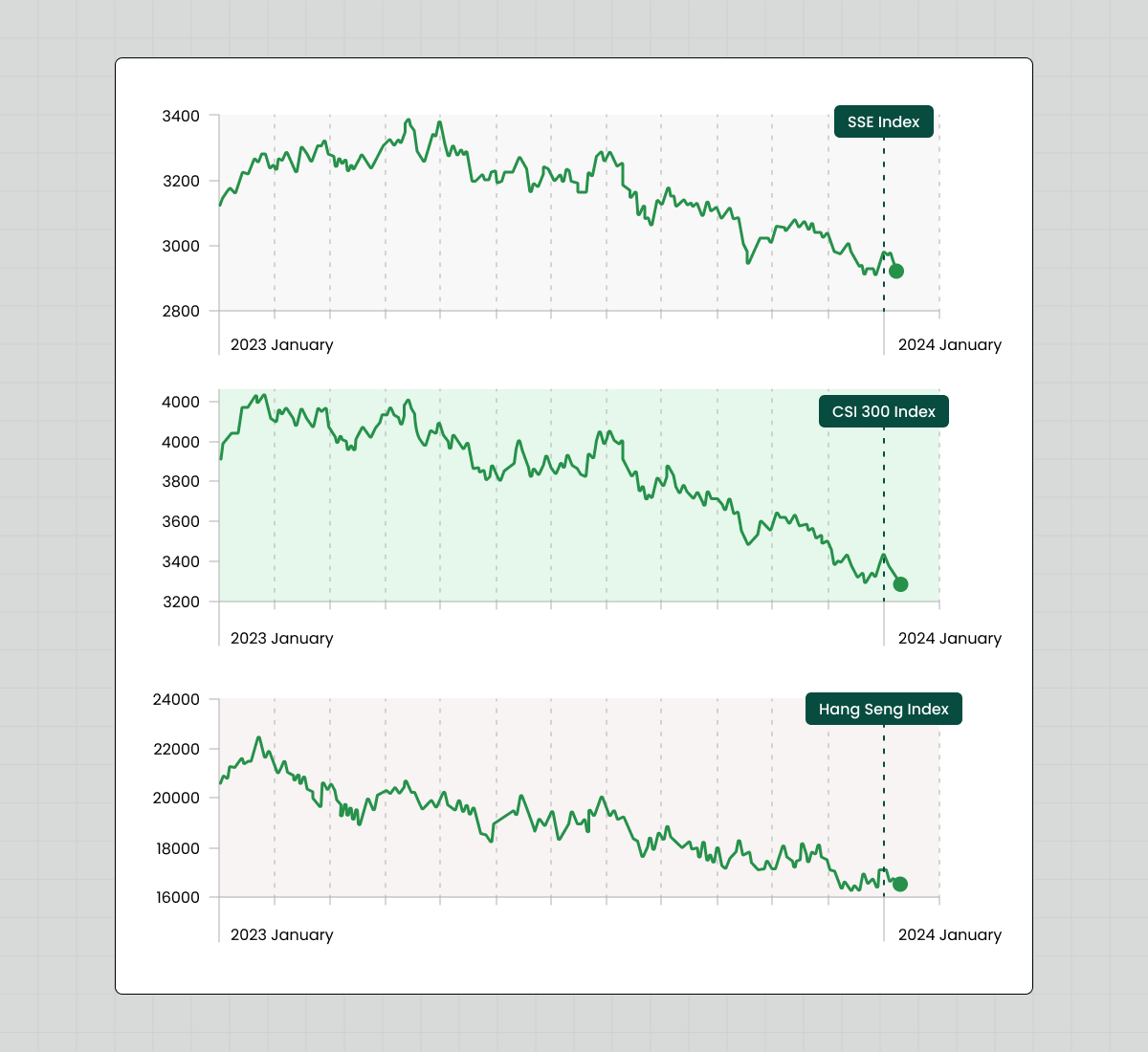
Against the backdrop of the COVID-19 pandemic, Chinese stocks fell to a historic low in the first part of this period, and stayed that way for several years.
The main driver of this plummet was that the government’s crackdown on tech in late 2020 tore the rug out from under the sector to the tune of over $1 trillion.
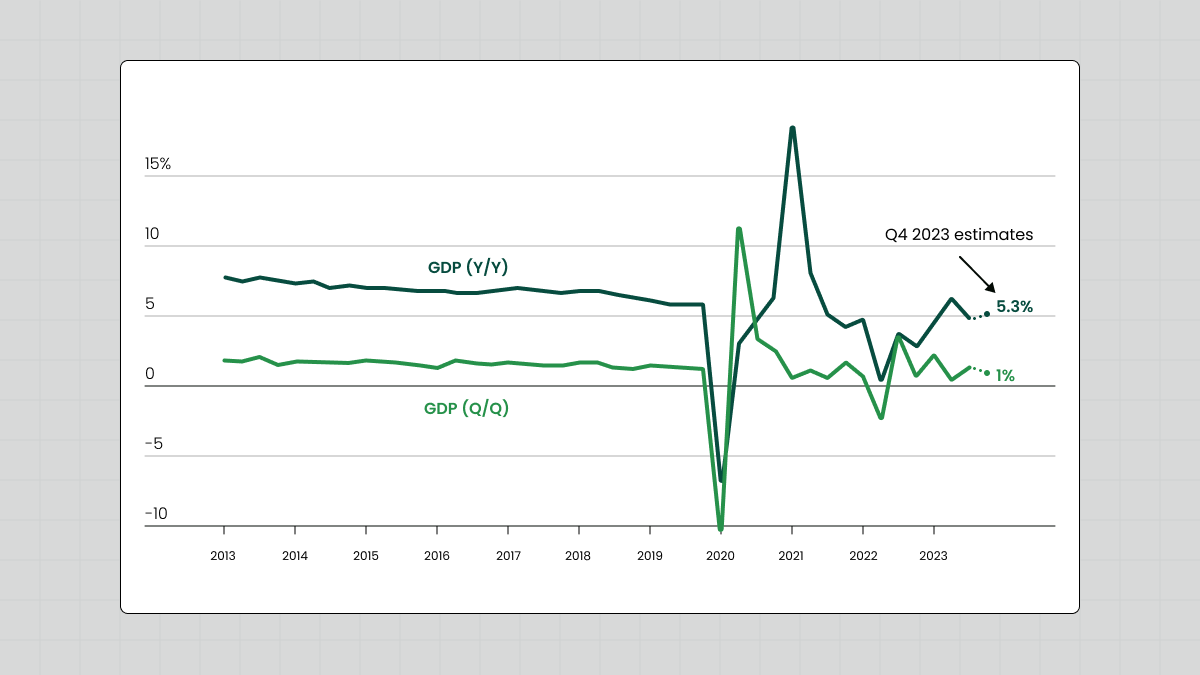
To add insult to injury, the government also instituted a strict zero-coupon policy, which meant the only way to profit was to buy low in an overbought market and wait for the price to stabilize. As a result, even with the lockdown being lifted in 2023 and businesses returning to operating, it took until mid-2025 to finally get the stock market rolling again.
In 2024, the Chinese Securities Regulatory Commission, headed by its new chief Wu Qing, started scrutinizing market practices more closely, due in no small part to the increasing tensions with the United States.
During this period, the Shanghai Composite and other major indices fell sharply, and major companies such as Great Wall Motor and Poly Real Estate experienced dramatic share price declines. For example, by January 2024, Great Wall Motor's shares had fallen 27.86%, and Poly Real Estate's shares had fallen 43.81%.
The government potentially invested as much as 2 trillion yuan from off-shore accounts belonging to state-owned enterprises (SOEs) into the market, but this only served to somewhat slow the pace of drowning - still quite far from a full bailout.